Aerodynamics
Avionics and Controls
Propulsion and Power
Systems Integration
Human Interface
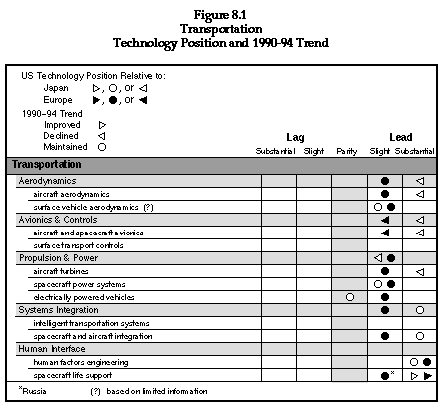
At a more specific technology level, the report discusses aircraft and surface vehicle aerodynamics, aircraft and spacecraft avionics, surface transportation controls, aircraft turbines and spacecraft power systems. At the level of systems integration and human-machine interface, the report discusses intelligent transportation systems, spacecraft and aircraft integration, human factors engineering (as it relates to transportation systems) and spacecraft life support systems.
The area of intelligent transportation systems is one where the U.S., Western Europe, and Japan are all engaged in various private and public efforts to develop more effective and efficient surface transportation systems. This area will ultimately involve radical changes in both vehicular technology and infrastructure that have the capacity to alter the American transportation system by better incorporating modern information technology into virtually every phase of passenger and freight transportation including its intermodal elements.
The U.S. has preeminence in most transportation areas, except for Western European developments in commercial aircraft technology, the leadership of France, Germany and Japan in fielding high speed rail systems, and German and Japanese advances in mag-lev technology. The specifics of the assessment are presented in the text of the section. The summary of the U.S. relative position and trends from 1990 to 1994 are shown in Figure 8.1.

Improved aerodynamics is critical to both commercial and military aircraft, including rotary wing aircraft. For commercial aircraft, improved aerodynamics reduces operating costs, thereby making the aircraft more competitive on international markets. It also significantly contributes to the national security by improving efficiency and performance of military aircraft.
Europe--primarily Germany, France, and the United Kingdom--is only slightly behind the United States in aircraft aerodynamics. Europe's hypersonic programs have been slowed significantly for economic reasons, but the test infrastructure continues to advance. European aerospace firms are investigating laminar flow airfoil technology to improve the competitiveness of their commercial aircraft. Current R&D efforts include the multinational European Laminar Flow Investigation (ELFIN) project which involves evolutionary improvements in and optimization of airfoil geometry as well as hybrid laminar flow techniques (HLFTs). Europe is conducting HLFT tests on the tail fin of an A320 and planning wingtip-to-wingtip tests on an A340. In addition, France's Dassault began HLFT tests in early 1993 on its Falcon 900 business jet. Airbus has also done extensive testing of riblets--originally developed by NASA and U.S. companies--on an A320 and A340 to create laminar flow over large regions of the aircraft's surface.
Japanese firms are substantially behind firms in both Europe and the United States, but joint work on the FS-X has allowed an infusion of U.S. aerodynamic technology that is improving their capabilities. Japanese research in laminar flow control has been limited by the lack of domestic commercial aircraft programs. Russia generally is behind the leaders in computational capability and advanced computational fluid dynamics codes for hypersonics and progress is slowing because of political and economic uncertainties. The United States also has a slight lead in technology for surface vehicle aerodynamics, based in large part on capabilities derived from the aerospace industry.
Avionics and Controls
The United States is the world leader in most avionics and
controls technology and is likely to maintain but not
increase its edge over the next several years. Two European
firms, France's Sextant Avionique and the UK's General
Electric Company (GEC), are challenging traditional U.S.
leaders across a wide range of avionics products but with the
current downturn in military budgets, commercial developments
will be slowed as few companies will be willing to risk large
investments solely for the commercial market. Fewer new
programs will make it difficult for foreign countries to
decrease the gap or for the United States to increase it.
During the 1980s, ring laser gyroscopes (RLGs)--first produced by U.S. firms for commercial aircraft--began replacing mechanical gyros in inertial navigation systems. During this same period, fiber-optic gyroscopes (FOGs) were also developed. Although FOGs initially promised equivalent performance to RLGs at lower cost, they have not yet met these expectations. Industry experts believe that FOGs are competitive in some low-to-medium-accuracy applications--such as attitude and heading indicators--but have not yet challenged RLGs in the high accuracy market. FOG systems-- updated by global positioning system satellites--offer some long-term promise, particularly if FOG drift rate reduction programs are successful.
Avionics technologies have a huge impact on military aircraft, and leadership in areas such as radar, fire- control, countermeasures, stealth, and command and control must be maintained for the implementation of national security policy and strategy. Avionics technologies also have a large effect on commercial aircraft, and this impact will grow in future years. Active controls technologies as pioneered by U.S. aircraft such as the F-16 are now providing reduced fuel consumption and maintenance costs for the European Airbus and other foreign competitors to U.S. commercial aircraft. Advanced cockpit displays and controls, such as the "glass cockpit" reduce crew expenses and increase safety. Rotocraft are also likely to benefit from advances in avionics leading to improved safety and efficiency. Upcoming advancements in air traffic technologies should permit increased airspace usage with greater safety. Integration of aircraft and air traffic control systems of the future will be key to reducing delays and increasing capacity.
Advanced avionics make a direct contribution to the competitiveness of U.S. aircraft on world markets. They certainly play an important role in the U.S. ability to meet its national security and warfighting objectives.
European firms are at parity with U.S. firms in fly-by-wire (FBW) technology and ahead in its application to commercial aircraft. Although FBW systems have been in use on military aircraft since the mid-1970s, they were not introduced on commercial transports until the mid-1980s. Operating costs and safety considerations drive commercial FBW applications through reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency, increased reliability, and less unscheduled maintenance. European success can be attributed to two factors --aggressive application of military flight control technology to commercial aircraft and a wave of consolidation within the avionics industries. Although FBW technology was originally developed by U.S. firms for military aircraft, European firms--Britain's GEC and France's Sextant--were the first to apply the technology to a commercial aircraft, the Airbus A320. In late 1990, GEC won the contract to supply the FBW system for the Boeing 777--the first U.S.-produced commercial aircraft to incorporate FBW technology. Because new commercial transport programs like the Boeing 777 are launched so infrequently, GEC is gaining a significant advantage over U.S. firms in the commercial application of FBW technology. Japan, by contrast, has only a basic capability in FBW technology, through the FSX fighter program, and currently lacks a commercial program to gain experience.
U.S. firms--led by McDonnell Douglas--appear to have the lead in fly-by-light (FBL) developments. Much of the impetus for the U.S. developments comes from ARPA's technology reinvestment program. Limited reporting indicates that GEC and France's Dassault lead the Europeans in FBL development. GEC gained important experience through the FBL system it built for a dirigible. Japan has shown interest in FBL, but has allocated relatively small budgets for its development. Further development in FBL technology will likely require an appropriate military program and will give the country sponsoring the effort a significant advantage in FBL technology. NASA AST FBL program is also a major contributor to this technology development for the civil sector.
The United States is the leader in ring laser gyro (RLG) technology but several foreign firms have developed strong RLG capabilities. British Aerospace and the French firms SAGEM and Sextant are producing RLGs with long-term drift rates adequate for aircraft navigation. Foreign firms, however, lag U.S. firms in reducing gyro size while maintaining high accuracy. Foreign firms also remain secondary players in the RLG market because they are not cost competitive with U.S. firms. As Sextant's RLG production technology matures, the firm may attempt to win navigation contracts for Airbus aircraft--currently supplied by Honeywell. Japan Aviation Electronics originally based its development of RLG technology on licenses from a U.S. firm but now has an independent capability in the technology. Future foreign RLG developments will depend on whether those firms continue to fund RLG research or change their focus to fiber optic gyroscope or the Global Positioning System (GPS). The United States has a slight lead in fiber optic gyroscopes--an alternative technology for aircraft inertial- grade accuracy. Foreign efforts include work by the French firm, Photonetics, and Japan Aviation Electronics. U.S. manufacturers retain a lead in global positioning systems (GPS) receivers and processing equipment, largely because of their experience developing the satellite system. Europeans and Japanese each have a number of firms working on GPS receivers, but industry experts predict the U.S. will maintain its position over the next several years.
Japanese firms do not have strong technical capabilities across broad product lines but are strong in avionics display technologies. Japanese firms such as Hosiden, Sharp, Hitachi, NEC, and Toshiba have very high production yields and account for 95 percent of the world's active matrix liquid crystal displays--the technology of choice for most high-performance flat panel display (FPD) applications. Cockpit displays have evolved over the last decade from complex electromechanical instruments to electronic multifunction displays. The most advanced current commercial aircraft have displays based on cathode ray tubes, but FPDs are lighter, take up less space, consume less power, and offer increased display areas. Japanese firms were the first to achieve FPD sizes large enough for aircraft, and are now selling them on the commercial market (Boeing 777). Japan's FPD producers have only limited interest in producing FPDs for avionics applications, primarily because production runs are very small relative to the large FPD orders for computer and consumer electronic applications. Over the next several years, the United States could close the technology gap with Japan, based on government support for FPD and manufacturing technology development.
Spacecraft avionics currently involves issues of reliability, space certification, miniaturization, reduced power consumption, and "black box" modularity. Spacecraft control systems, on-board navigation systems, and precise engine throttling would all benefit from further improvements in this area. There is a growing trend towards the standardization and assembly of building block components to achieve a number of different functions and in this way to avoid a requirement to develop a large quantity of special purpose systems.
Efficiency of aircraft turbines significantly affects purchase price and operating costs of aircraft. Improved engines contribute to job creation in the aerospace sector, as well as to the competitiveness of the U.S. aerospace industry, because the U.S. is a major player in international aerospace markets. They also contribute to improvements in environmental quality by reducing emissions from aircraft engines and reduced energy consumption. Greater efficiency of aircraft engines also contributes to the warfighting capability of rapid global power projection.
The United States has the overall lead in aircraft turbine engine technology, based on its superior military technology, but shares the lead in commercial propulsion systems technology with the UK's Rolls Royce. Europe has an edge in facilities for propulsion/airframe integration testing of large models at high Reynolds Numbers. They may also have an edge in technologies for noise reduction. Second-tier manufacturers in France, Germany, and Japan have seen their capabilities increase through international joint ventures and European military development programs. This general pattern is likely to continue with France (likely to become more competitive with the United States over the next five years as they assume responsibilities for a greater percentage of engine designs and component manufacturing) leading the way and Japan bringing up the rear. While Japan will likely become a more attractive joint venture partner-- almost certainly the country's prime goal--technology transfer is unlikely to be enough to significantly alter capabilities relative to the world leaders over the next several years.
Because of the trend towards higher thrust engines, in concert with the trend towards larger aircraft, by the year 2000, deliveries of engines with greater than 45,000 lb thrust are forecast to be more than 50 percent of the market by value. The trend towards higher-thrust engines has two general consequences for the competitiveness of engine manufacturers. The higher costs associated with development of these large engines have led to more joint international programs and transfer of technology to second-tier manufacturers. Secondly, with the attention of the technology leaders focused at the high-thrust end of the market, second-tier manufacturers are increasing their roles in the development of smaller engines. This is particularly true of the French firm SNECMA, which has recently announced its intention to lead the development of a new turbofan for civil applications based around the core of its latest fighter engine.
Performance improvements in propulsion systems are driven by core technology advances in engine component technologies, manufacturing capabilities, and systems integration. Europe continues to lag in turbine-blade technologies, but is keeping pace with U.S. developments. The United Kingdom and France are slightly behind the U.S., but have introduced some technologies first. For example, the United Kingdom was the first to introduce hollow fan blades, instrumental for reducing engine weight. France is a leader in advanced composite materials and has introduced silicon carbide nozzle flaps for their M88 engine.
Wide-chord fans--which do not require part-span shrouds and are therefore more efficient--are quickly being adopted industry-wide. Some operators of engines with wide-chord fans have also claimed that the fan blades' ability to flex makes them more resistant to birdstrike damage. Next generation engines will likely also incorporate swept aerodynamics in both fans and compressors to provide additional increases in efficiency. High strength-to-weight compressor materials are being developed to permit increased rotational speeds that--along with the adoption of low aspect ratio blade shapes--will enable reductions in the number of airfoils required.
Rolls Royce's development of the wide-chord fan gave it a technology lead in this area, but U.S. firms reacted quickly to close the gap and are likely to move ahead over the next several years, as composite fan blades are introduced on the GE90 and Pratt and Whitney's Advanced Ducted Prop engine. Research and development of active compressor stability control and high strength-to-weight ratio materials-- including metal matrix composites--proposed by the European Aero-Engine Industry Group parallel U.S. efforts. Japan's responsibility within the IAE consortium for the fan and low pressure compressor is its first major share of a commercial engine program. Although the fan was derived from an existing Rolls Royce design, it is worth noting that the V2500 passed every ingestion and fan-blade-off test the first time the engine was tested. Despite this improvement, problems experienced on other indigenous efforts suggest that Japan still has a substantial technology lag.
Rolls Royce combustor technology is at parity with that of U.S. manufacturers; however, the company slightly lags in the application of turbine technology to commercial engines. Its latest civil engine offering--the Trent--still uses directionally solidified high-pressure turbine blades. While Rolls Royce and the UK Ministry of Defense are jointly funding high-pressure turbine design research, improvements resulting from this program will likely be offset by advances already achieved in a similar U.S. effort. Japan's responsibility for the low-pressure turbine on the GE90 program complements its role in the IAE consortium.
Rolls Royce now uses full authority digital engine controls (FADECs) on all of its engines and France has demonstrated improvement through production of a FADEC for SNECMA's latest military engine and controls components for the CFM56 and CF6-80. Japan has an indigenously developed FADEC that has reportedly been successfully ground and flight tested. However, the system is intended for use on the FSX fighter and has yet to be validated in service.
Space power systems are relevant to both economic progress and national security. They contribute to sustainable economic growth through promoting efficient energy production and utilization technology, and help the environmental monitoring and assessment function through their ability to provide long term power for environmental monitoring satellites. They contribute to national security through their ability to provide energy sources for military surveillance systems.
The U.S. is preeminent in spacecraft power systems, based largely on the relative scale and sophistication of its space effort. Only the U.S. and Russia are manufacturing radioisotope thermal generators (RTGs) essential for the space mission to the planets, but there is a possibility that the U.S. will abandon research in this technology.
The following areas are currently being emphasized in ITS research:
In addition to these six major areas, electronic payment services would improve convenience and efficiency, for toll collection, personal vehicle use, interstate tracking, and for public transit users who might rely on "smart" fare cards. Some of these systems are already fielded around the country.
Forecasts suggest that traffic fatalities, accidents and congestion would markedly decrease when ITS becomes operational. In fact, successful deployment of ITS has the potential to vastly improve surface transport in the U.S. while improving energy efficiency and reducing pollution from transportation. Although much of ITS progress thus far has targeted private and commercial motor vehicles, it is expected that rail system and public transportation operations will also benefit. Although the major benefits would promote health, safety, and economic security, important national security benefits would stem from more efficient use of existing highways in times of crisis or war.
There seems to be no clear leader in intelligent transportation systems technologies since the U.S., Western Europe, and Japan are all pursuing active programs involving both private and public resources.
One emerging tool for enhanced systems integration is multidisciplinary design optimization. It is an emerging computational technique which has high promise for the overall improvement of design quality and resulting aircraft efficiency. It includes several numerical techniques for finding an optimal system solution across numerous functional disciplines such as aerodynamics, structures, and controls. While this has always been a goal, attacked by such time- honored techniques as the carpet plot, it has been virtually impossible to simultaneously optimize any complex system due to the number of variables required.
Multidisciplinary Optimization techniques such as "Decomposition" hope to break this logjam and allow complex system optimization of hundreds or thousands of variables. This will find more-optimal solutions resulting in lower aircraft weight and cost. Lower weight and cost will, in turn, improve the competitiveness of U.S. aircraft on world markets, and will result in aircraft which are more friendly to the environment because they will use less fuel and producing fewer emissions. In addition, multidisciplinary aircraft design will allow designers to produce better military aircraft, contributing to national security and warfighting capabilities.
Europe is slightly behind the United States in overall systems integration capability for civil and military aerospace systems. With the development of the Boeing 777, the United States took the lead in the design and manufacture of commercial aircraft. Boeing used an integrated approach through fully digital product definition with all parts created by CATIA CAD/CAM systems. Airbus has not yet used this approach and may not for the next several years. However, Europe does have the capability to integrate increasingly complex aircraft systems as demonstrated in a host of commercial and military aircraft. Japan, on the other hand, has not yet led a major commercial development and has had difficulty with systems integration on its military programs. Japanese firms, although members of Boeing's design team, have not independently designed and manufactured their own modern commercial aircraft. Japan also trails the United States and Europe in spacecraft systems integration capability, including satellites and launch vehicles.
The willingness to use and perhaps depend on technology is a cultural phenomena not simply bounded by the basic technology. A primary case in point is the degree of automation entailed in the Airbus flight control systems. As automation becomes more capable, the degree of keeping humans in the control loop and the ability to over-ride the control system will become more of an issue. In the case of highly unstable, non-linear control regimens where computer control is the only option, operator training and operator acceptance pose difficult problems - particularly as to the judgment of when and how to over-ride.
For the surface vehicle driver, creating a good interface may involve ergonomic design, and integration with systems that are likely to be part of the intelligent transportation system of the future. As part of an initiative to improve the safety and efficiency of the nations highways, work has been done to provide in-vehicle signing information and safety warning systems, sensory systems which provide extended line of sight during reduced visibility conditions, and obstacle detection and avoidance systems. This is intended to lead up to a fully automated highway system.
High "g" loads experienced by military pilots reduce the availability of well oxygenated blood to the retina, resulting in gray out and a tunneling of vision, and eventually loss of blood flow to the brain resulting in loss of consciousness. Countermeasures using small ultrasonic transducers are able to sense the reversal of blood flow at high "g" and used to control the pressure in a lower body garment intended to restrict the pooling of blood in the lower abdomen and legs. Lessons learned from the deterioration of the visual field under high "g" loads have also been applied to instrument design, head-up-displays, and alarm systems intended to catch a pilots attention even in a high noise, high stimulus environment.
Meaningful analog studies on Earth and in space are required for long duration flights. Ongoing work using the Antarctic as an analog has been quite productive. Another challenge facing crews in remote, isolated situations is that abnormal maladaptive behavior due to exposure to toxic substances may be indistinguishable from psychosis. Senior observers of military and exploration efforts have pointed out that human factors were responsible for mission failure more often than equipment factors. As in most complex systems, habitability and ergonomics also require more support and integration into spacecraft systems design.
Research, development and testing of human factors and the underlying assessment technologies based on physiological measurements has been conducted by the U.S. national laboratories, and their associated universities and contractors. Individual private corporations have conducted little work in this area beyond noise reduction and seating design; focusing more on appealing to consumer interest than in functional design issues. Automotive manufacturers here and abroad have demonstrated many concept vehicles with alternative interior and gauge designs; but these tend to driven more on visual graphic impact than meaningful contributions to improved human performance or control. Ergonomics has been most extensively studied and reduced to practice in the past by the Europeans, but as its value for differentiating consumer products has been more widely acknowledged in the past few years, manufacturers are beginning to draw on the established data bases.
The U.S. has a clear-cut lead in anti-g countermeasures in high performance aircraft, and even cockpit display and instrumentation. As the pressure suits universally worn by fighter pilots are capable of being pressurized, it is more of a deployment decision rather than one of underlying technology. The ultrasonic Doppler flow techniques for assessing individual pilot status during high-g have been more fully evaluated, control algorithms refined and reduced to practice in the U.S.
In the broader perspective of the many sub-systems which comprise an integrated life support system, the Space Shuttle Extended Duration Orbiters provide an example at the 14 to 17 day end of the scale, with the pending Space Station exemplifying low development risk systems which can be ready evolved once the basic operational platform is in orbit. The critical areas include atmosphere control and supply, atmosphere revitalization, potable and wash water systems, waste management systems, temperature and humidity control, water recovery and management, microbial and toxics decontamination, and fire detection and suppression. All of these sub-systems are designed to evolve during the lifetime of the station, with eventual closure of the air, water, and potentially even the food loop as goals for long duration space flight. As designed, the base-lined filtration systems will be swapped out every 30 days with a 90 day resupply cycle from the ground. Water and CO2 scrubber systems now in development could have their mass significantly reduced but with a corresponding increase in their power requirement.
Pilot plant evaluation, scale-up, and in-space validation must be performed under actual operating conditions, in zero gravity or on the Lunar surface. Lunar validation of such systems should precede any situation of long-term dependency. Advances in this area would contribute to maintaining leadership of the U.S. in science, mathematics, and engineering by improving our ability to facilitate long term space flight and by facilitating closed loop processing of materials with minimal environmental impact.
As the Russian "Mir" is the only permanently manned platform currently in space, it provides an example of the capabilities of water recycling and CO2 removal but with total dependency on ground based resupply of oxygen. The Russians systems which have been of particular interest, water recycling and CO2 removal, are the subject of a contractual relationship between Hamilton-Standard (one of the U.S. companies with a long-term involvement in this area) and the Russia groups. Several studies have been performed to assess the utility of the Russian work for early Station configurations.